Exploring .NET and Its Use in Building Scalable Applications

Nowadays, software that grows along with the business is demanded by enterprises. Here enter .NET scalable applications. The applications built with .NET are supposed to be high-performing as usage grows. Whether you are developing internal software or consumer-facing applications, .NET offers the right tools to engineer solutions scaling on the vertical level, i.e., on more powerful hardware, and horizontal level, i.e., across multiple servers, to meet the increased user demand. Given its mature frameworks and performance optimizations, .NET has established itself in large systems, thus becoming the preferred candidate for enterprise-level applications needing reliability under load and swift execution.
Notably, .NET’s benefits are industry-agnostic. It powers systems across Healthcare & Life Sciences, E-Commerce & Retail, Finance, Education, Travel and Hospitality, Telecommunication, Logistics and Transportation, Manufacturing and Construction, Gaming, and more. From online banking platforms to large e-commerce sites, .NET’s robust architecture supports growing user bases without a hitch.
Why .NET for Enterprise-Grade Scalable Applications
.NET for enterprise apps is a natural fit when scalability and reliability are top priorities. According to Microsoft, “.NET emerges as an advantageous platform for building enterprise applications, since scalability and performance are the two considerations.” Hence, from its runtime optimizations with just-in-time generation and efficient memory management, `RunIt` ensures high performance, also enabling cross-platform support since modern .NET runs and supports implementations from Windows, Linux, to macOS, and is equipped with strong security. .NET along with Azure can make the livelihood of deployment for scalable .NET applications easier by providing capabilities along with auto-scaling and load balancing. This mix of performance, portability, security, and cloud-friendliness makes .NET the go-to platform for enterprises when building their demanding applications.
Scalable Architecture with .NET: Microservices and Cloud
One proven strategy for achieving a scalable architecture with .NET is adopting microservices. In a microservices architecture, an application is split into small, independent services (unlike a monolith, where everything is one unit). Companies like Netflix and Amazon have famously used microservices to achieve large scale, and the .NET platform provides the tools to do the same.
.NET is well-suited for microservices because of its efficiency and flexibility. For example, ASP.NET Core’s Kestrel web server can handle thousands of requests per second with low latency, so each service can manage substantial load independently. .NET also has excellent container support (official Docker images and a small runtime footprint), making it easy to deploy many services in the cloud. With orchestrators like Kubernetes, a .NET microservices system can automatically scale each component to meet demand.
.NET Core vs .NET 7 Scalability
.NET 7 introduced major performance improvements over earlier .NET Core versions. For instance, on an 80-core server, ASP.NET Core handled 514% more requests per second after .NET 7’s optimizations (jumping from 2.4 million to 14.6 million RPS). With enhancements in thread pooling and garbage collection, .NET 7 utilizes modern hardware far more efficiently. In short, applications on .NET 7 can serve significantly more concurrent users than on older versions. Upgrading from legacy .NET Framework or early .NET Core to the latest version thus directly boosts an app’s scalability.
Best Practices for Building Scalable Web Apps in .NET
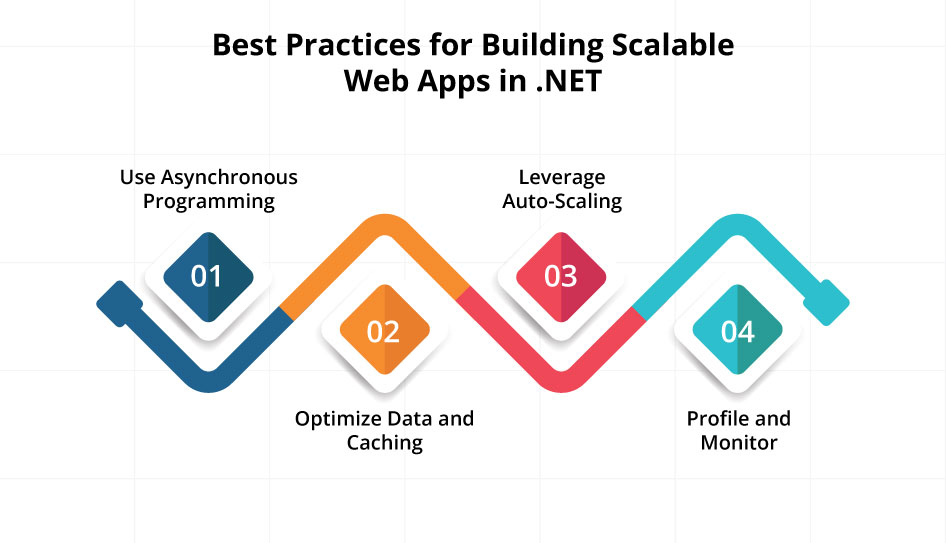
To ensure your .NET scalable applications can handle growth, consider these best practices for building scalable web apps in .NET:
- Use Asynchronous Programming: Embrace async/await for any I/O-bound operations (database calls, API calls, file access). Asynchronous code frees up threads to handle other requests while waiting on I/O, allowing your app to serve more users concurrently. In ASP.NET Core, avoid blocking calls and prefer non-blocking, event-driven designs – this is fundamental to scalability.
- Optimize Data and Caching: The database can become a bottleneck as traffic grows. Use efficient queries and proper indexing to keep database operations fast. Also cache frequently used data or results of expensive queries. .NET makes it straightforward to use in-memory caches or distributed caches like Redis, which can greatly reduce database load and response times. By optimizing your data layer and using caching, you prevent slow database calls from dragging down your application under scale.
- Leverage Auto-Scaling: Deploy your .NET application on infrastructure that supports auto-scaling and load balancing (e.g., Azure App Services, AKS, AWS ECS/EKS). Configure auto-scale rules so that when traffic spikes, new instances spin up automatically. Likewise, use load balancers to distribute requests evenly. Cloud auto-scaling ensures high availability and performance during peak loads without manual intervention.
- Profile and Monitor: Use profiling tools and APM (Application Performance Monitoring) to find performance bottlenecks in your .NET code. Identify slow methods or heavy memory usage and optimize them (through better algorithms, caching, etc.). Monitor key metrics like response times, CPU, memory, and error rates in production. Maintaining performance is an ongoing process – continuous monitoring and tuning will help your system stay scalable as it grows.
By following these best practices, building scalable web apps in .NET becomes much more achievable. A combination of non-blocking code, judicious caching, efficient data access, and cloud-based scaling can enable an ASP.NET Core application to handle dramatic traffic increases gracefully. Scalability isn’t an afterthought – it’s built into the design from the start.
Conclusion
Scalability isn’t just about handling traffic spikes; it’s about preparing your applications to support long-term growth, innovation, and resilience. With .NET, enterprises gain a trusted foundation that combines performance, flexibility, and security to meet future demands head-on.
At FX31 Labs, we don’t just build software; we architect systems designed to evolve with your business. From custom enterprise application development and MVP development to generative AI-enabled software solutions, our team ensures your .NET applications are future-ready and built to scale seamlessly.
Ready to transform your ideas into scalable, high-performing applications?
Let’s talk about how FX31 Labs can power your next .NET project.
FAQs
1. How do microservices help scale .NET applications?
Microservices architectures help increase scalability by allowing different components of an application to scale independently. In .NET, you could split an app into services for specific domains (user accounts, orders, payments, and so on). So, if under load one service becomes a hotspot, you just add more instances of it, while leaving other parts of the system intact. .NET fast networking and its native support for containerization further make it easy for these services to communicate among themselves and scale under load together.
2. What are some best practices to make a .NET web app scale better?
Consider asynchronous programming for any operation likely to block so that the server works on other things in the meantime. Use caching as far as possible so that time-consuming calculations or database queries are not carried out per request. Make your application database-friendly; that is, fetch only what is needed and use indexing to speed up your database queries. Then, please design your application so that it is modular/microservice-oriented, enabling you to scale out any component as necessary. Finally, consider running your application on any cloud platform with auto-scaling and load balancing, coupled with continuous monitoring of the app to promptly detect and fix any performance issues.
3. Differences between vertical and horizontal scaling in .NET?
Vertical scaling means adding more punch to your .NET app via tougher hardware (more CPU/RAM, for instance). Horizontal scaling means multiple instances running across servers. Both may work, yet for enterprise apps, horizontal scaling is usually a more reliable and cost-effective option, provided you have a load balancer.
4. Is .NET 7 always better for scalability compared to older versions?
Yes, in most cases. .NET 7 includes significant performance improvements, such as better garbage collection, thread pooling, and runtime optimizations. These allow .NET apps to handle more requests per second compared to .NET Core or older frameworks. Upgrading is usually worth it if scalability and performance are priorities.
5. How does performance tuning work in .NET applications?
Performance tuning involves profiling your app to find bottlenecks (slow code, inefficient queries, memory leaks) and optimizing them. In .NET, this might mean using async patterns, reducing allocations, caching results, or improving database calls. Tools like Application Insights or New Relic can help monitor performance and guide improvements.
